#React常用类型
预计阅读时间: 5 分钟#react+ts必备:react中常用的ts类型
- React.FC的注解是有些问题的,在是否优先使用这个类型作为注解上存在一部分争议,因为这个类型破坏了JSX.LibraryManagedAttributes, 导致其忽略了函数和类组件的defaultsProps,displayName这样的参数 (详见:https://github.com/typescript-cheatsheets/react/issues/87)。另外,其不能像class组件一样返回props的children (详见:https://github.com/DefinitelyTyped/DefinitelyTyped/issues/33006) ,显式的定义children属性,或更改源码可解决这个问题。
还有一点,FC在@types/react18之前总是隐式的定义好children,即使你的Props注解并没有定义children,你仍然可以在参数里解构出它。
-
在@types/react版本16.8和18之间可以使用React.VoidFunctionComponent或React.VFC替代 React.FC ,它规定要想在函数体内使用props必须显示的定义它
-
因为编译器的限制 在函数组件中,不能返回除jsx和null以外的值,如果真的需要返回除这两种之外的值,可以使用类型断言,例如
const MyArrayComponent = () => (Array(5).fill(<div/>) as any) as JSX.Element
- 函数组件和类组件的常用注解
// 函数 React.FC<Props>;
// 类 React.Component<Props,state>
- 如何开发泛型class组件,在使用的时候约束它的props类型
type SelectProps<T> = {items: T[]};
class Select<T> extends React.Component<SelectProps<T>, {}> {
//...
}
const Form = () => <Select<string> items={['a','b']}>
- 开发泛型函数组件
function foo<T>(x:T): T{
return x
}
// 注:如果是箭头函数需要用extends提示编辑器这是个泛型
// const foo = <T extends Record<string,unknow>>() => {}
7.React.ReactElement可以通过传入泛型,来注解类或函数组件的实例化结果,相当的好用
class MyAwesomeComponent extends React.Component {
render() {
return <div>Hello</div>;
}
}
const foo: React.ReactElement<MyAwesomeComponent> = <MyAwesomeComponent />; // Okay
const bar: React.ReactElement<MyAwesomeComponent> = <NotMyAwesomeComponent />; // Error
- 优雅地注解useState
const [user,setUser] = React.useState<IUser | null>(null);
const [user,setUser] = React.useState<IUser>({} as IUser)
- reducer的注解
import { Reducer } from 'redux';
export function reducer: Reducer<AppState, Action>() {
}
10.优雅地注解useRef
// 如果可以的话尽量使用的类型具体点
// 比如使用HTMLDivElement 就比HTMLElement好很多,比Element好更多
function Foo(){
const divRef = useRef<HTMLDivElement>(null);
return <div>etc<div/>
}
11.类型断言
1.as
2.泛型注解(React的jsx里用不了)
3.去除null或undefined的非空断言
- 函数的执行结果在给其他变量进行赋值,会发现该变量的注解有问题
function fn(){
return ['1',false]
};
type AType = string[]
let a:AType = fn() // error
// 解决办法:
// 1.将其变为 return ['1',false] as any[] 或者 return ['1',false] as string[],如果是只读的可以 as const
// 2. type Atype = (string | boolean)[],但已不符合实际意义
// 3. react团队推荐自定义钩子return两个以上的值时可以使用对象
13.createContext
type Theme = 'light' | 'dark'
const TeemeContext = React.createContext<Theme>('dark')
// 创建{}用断言 const Context = React.createContext({} as ContextState);
const sampleAppContext: TeemeContext = 'light';
export const App = () => (
<AppCtx.Provider value={sampleAppContext}>...</AppCtx.Provider>
);
// 如果想创建默认值为null或undefined可以React.createContext<string>(undefined!),不然在使用.时
// 会报没有相关api可以调用,但这样失去了类型安全,或者可以使用一个helper函数来帮助我们创建,让我们不再考虑undeined
// 的情况
function createCtx<A extends {} | null>() {
const ctx = React.createContext<A | undefined>(undefined);
function useCtx() {
const c = React.useContext(ctx);
if (c === undefined)
throw new Error("useCtx must be inside a Provider with a value");
return c;
}
return [useCtx, ctx.Provider] as const; // 'as const' makes TypeScript infer a tuple
}
// Usage:
// We still have to specify a type, but no default!
export const [useCurrentUserName, CurrentUserProvider] = createCtx<string>();
function EnthusasticGreeting() {
const currentUser = useCurrentUserName();
return <div>HELLO {currentUser.toUpperCase()}!</div>;
}
function App() {
return (
<CurrentUserProvider value="Anders">
<EnthusasticGreeting />
</CurrentUserProvider>
);
}
//
// 整合useContext,createContext,useState为一体
export function createCtx<A>(defaultValue: A) {
type UpdateType = React.Dispatch<
React.SetStateAction<typeof defaultValue>
>;
const defaultUpdate: UpdateType = () => defaultValue;
const ctx = React.createContext({
state: defaultValue,
update: defaultUpdate,
});
function Provider(props: React.PropsWithChildren<{}>) {
const [state, update] = React.useState(defaultValue);
return <ctx.Provider value={{ state, update }} {...props} />;
}
return [ctx, Provider] as const; // alternatively, [typeof ctx, typeof Provider]
}
// usage
const [ctx, TextProvider] = createCtx("someText");
export const TextContext = ctx;
export function App() {
return (
<TextProvider>
<Component />
</TextProvider>
);
}
export function Component() {
const { state, update } = React.useContext(TextContext);
return (
<label>
{state}
<input type="text" onChange={(e) => update(e.target.value)} />
</label>
);
}
//更好的createContextApi
https://gist.github.com/sw-yx/f18fe6dd4c43fddb3a4971e80114a052
- useImperativeHandle, forwardRef
export interface MyInputHandles {
focus(): void;
}
const MyInput: RefForwardingComponent<MyInputHandles, MyInputProps> = (props, ref) => {
const inputRef = useRef<HTMLInputElement>(null);
useImperativeHandle(ref, () =>({
focus: () => {
if(inputRef.current) {
inputRef.current.focus();
}
}
}))
return <Input {...props} ref={inputRef}>
}
export default forwardRef(MyInput)
-
在继承 React.Component时,为了更好的注解state可以在 React.Component 和 **state:MyState {}**两处做注解,因为这两处分管不同
-
props的注解不用标记readOnly 。 因为在添加到泛型组件时,会自动添加ReadOnly
-
class组件 properties可以在声明时这样注解
pointer: number
- getDerivedStateFromProps
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props:Props, state:State): Partial<State> | null {
}
- 当您需要函数的返回值确定状态时可以使用ReturnType
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props:Props, state:State): Partial<State> | null {
}
-
ts中就你就可以不用写defaultProps了
-
如何优雅的取出component的props的注解
const GreetComponent = ({ name, age }: {name:string, age:25}) => (
<div>{`Hello, my name is ${name}, ${age}`}</div>
);
type ComponentProps<T> = T extends
| React.ComponentType<infer P>
| React.Component<infer P>
? JSX.LibraryManagedAttributes<T, P>
: never;
const TestComponent = (props: ComponentProps<typeof GreetComponent>) => {
return <h1 />;
};
22.
type AppProps = {
message: string;
count: number;
disabled: boolean;
/** array of a type! */
names: string[];
/** string literals to specify exact string values, with a union type to join them together */
status: "waiting" | "success";
/** any object as long as you dont use its properties (NOT COMMON but useful as placeholder) */
obj: object;
obj2: {}; // almost the same as `object`, exactly the same as `Object`
/** an object with any number of properties (PREFERRED) */
obj3: {
id: string;
title: string;
};
/** array of objects! (common) */
objArr: {
id: string;
title: string;
}[];
/** a dict object with any number of properties of the same type */
dict1: {
[key: string]: MyTypeHere;
};
dict2: Record<string, MyTypeHere>; // equivalent to dict1
/** any function as long as you don't invoke it (not recommended) */
onSomething: Function;
/** function that doesn't take or return anything (VERY COMMON) */
onClick: () => void;
/** function with named prop (VERY COMMON) */
onChange: (id: number) => void;
/** alternative function type syntax that takes an event (VERY COMMON) */
onClick(event: React.MouseEvent<HTMLButtonElement>): void;
/** an optional prop (VERY COMMON!) */
optional?: OptionalType;
};
23.
export declare interface AppProps {
children1: JSX.Element; // bad, doesnt account for arrays
children2: JSX.Element | JSX.Element[]; // meh, doesn't accept strings
children3: React.ReactChildren; // despite the name, not at all an appropriate type; it is a utility
children4: React.ReactChild[]; // better, accepts array children
children: React.ReactNode; // best, accepts everything (see edge case below),but {} as children is not supported
functionChildren: (name: string) => React.ReactNode; // recommended function as a child render prop type
style?: React.CSSProperties; // to pass through style props
onChange?: React.FormEventHandler<HTMLInputElement>; // form events! the generic parameter is the type of event.target
// more info: https://react-typescript-cheatsheet.netlify.app/docs/advanced/patterns_by_usecase/#wrappingmirroring
props: Props & React.ComponentPropsWithoutRef<"button">; // to impersonate all the props of a button element and explicitly not forwarding its ref
props2: Props & React.ComponentPropsWithRef<MyButtonWithForwardRef>; // to impersonate all the props of MyButtonForwardedRef and explicitly forwarding its ref
}
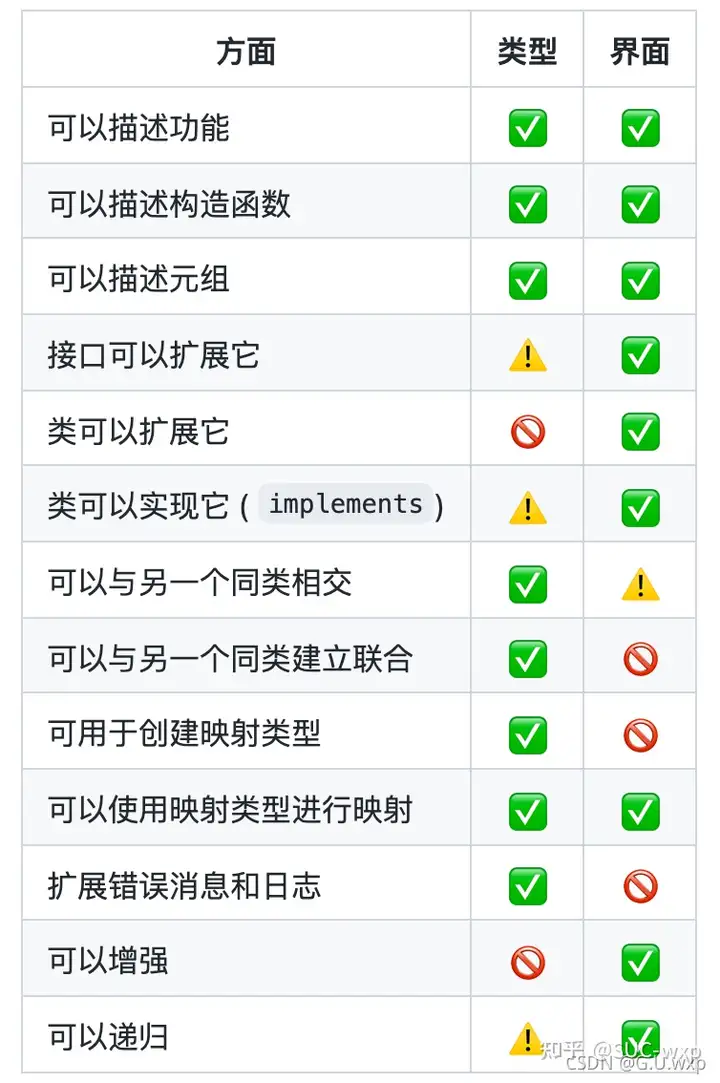
24.接口与类型别名的差异
类型别名和接口非常相似,在很多情况下你可以自由选择它们。
几乎所有的功能都在interface中可用type,关键区别在于不能重新打开类型以添加新属性与始终可扩展的接口。
25.当你想要使用getDerivedStateFromProps的返回值作为组建的state注解时
// 1. 普通情况
class Comp extends React.Component<
Props,
ReturnType<typeof Comp["getDerivedStateFromProps"]>
> {
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props: Props) {}
}
// 2. 返回函数
type CustomValue = any;
interface Props {
propA: CustomValue;
}
interface DefinedState {
otherStateField: string;
}
type State = DefinedState & ReturnType<typeof transformPropsToState>;
function transformPropsToState(props: Props) {
return {
savedPropA: props.propA, // save for memoization
derivedState: props.propA,
};
}
class Comp extends React.PureComponent<Props, State> {
constructor(props: Props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
otherStateField: "123",
...transformPropsToState(props),
};
}
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props: Props, state: State) {
if (isEqual(props.propA, state.savedPropA)) return null;
return transformPropsToState(props);
}
}
- 表单事件
// 如果不考虑性能的话,可以使用内联处理,注解将自动正确生成
const el = (
<button onClick=(e=>{
//...
})/>
)
// 如果需要在外部定义类型
handlerChange = (e: React.FormEvent<HTMLInputElement>): void => {
//
}
// 如果在=号的左边进行注解
handlerChange: React.ChangeEventHandler<HTMLInputElement> = e => {
//
}
// 如果在form里onSubmit的事件,React.SyntheticEvent,如果有自定义类型,可以使用类型断言
<form
ref={formRef}
onSubmit={(e: React.SyntheticEvent) => {
e.preventDefault();
const target = e.target as typeof e.target & {
email: { value: string };
password: { value: string };
};
const email = target.email.value; // typechecks!
// etc...
}}
>
<div>
<label>
Email:
<input type="email" name="email" />
</label>
</div>
<div>
<input type="submit" value="Log in" />
</div>
</form>
- 事件类型列表
AnimationEvent : css动画事件
ChangeEvent:<input>, <select>和<textarea>元素的change事件
ClipboardEvent: 复制,粘贴,剪切事件
CompositionEvent:由于用户间接输入文本而发生的事件(例如,根据浏览器和PC的设置,如果你想在美国键盘上输入日文,可能会出现一个带有额外字符的弹出窗口)
DragEvent:在设备上拖放和交互的事件
FocusEvent: 元素获得焦点的事件
FormEvent: 当表单元素得失焦点/value改变/表单提交的事件
InvalidEvent: 当输入的有效性限制失败时触发(例如<input type="number" max="10">,有人将插入数字20)
KeyboardEvent: 键盘键入事件
MouseEvent: 鼠标移动事件
PointerEvent: 鼠标、笔/触控笔、触摸屏)的交互而发生的事件
TouchEvent: 用户与触摸设备交互而发生的事件
TransitionEvent: CSS Transition,浏览器支持度不高
UIEvent:鼠标、触摸和指针事件的基础事件。
WheelEvent: 在鼠标滚轮或类似的输入设备上滚动
SyntheticEvent:所有上述事件的基础事件。是否应该在不确定事件类型时使用
// 因为InputEvent在各个浏览器支持度不一样,所以可以使用KeyboardEvent代替
28.createRef与forwardRef
class CssThemeProvider extends React.PureComponent<Props> {
private rootRef = React.createRef<HTMLDivElement>(); // like this
render() {
return <div ref={this.rootRef}>{this.props.children}</div>;
}
}
// 这样的forwardRef是可变的,可以在需要的时候给它赋值
type Props = { children: React.ReactNode; type: "submit" | "button" };
export type Ref = HTMLButtonElement;
export const FancyButton = React.forwardRef<Ref, Props>((props, ref) => (
<button ref={ref} className="MyClassName" type={props.type}>
{props.children}
</button>
));
// 如果希望它不可变
// type Ref = HTMLButtonElement
// (props, ref: React.Ref<Ref>) =>
// 如果你希望抓取forwardRef组件的props,可以使用compoentPropsWithRef
29.ReactDOM.createPortal
// Class
const modalRoot = document.getElementById("modal-root") as HTMLElement;
// assuming in your html file has a div with id 'modal-root';
export class Modal extends React.Component {
el: HTMLElement = document.createElement("div");
componentDidMount() {
modalRoot.appendChild(this.el);
}
componentWillUnmount() {
modalRoot.removeChild(this.el);
}
render() {
return ReactDOM.createPortal(this.props.children, this.el);
}
}
// hooks
import React, { useEffect, useRef } from "react";
import { createPortal } from "react-dom";
const modalRoot = document.querySelector("#modal-root") as HTMLElement;
const Modal: React.FC<{}> = ({ children }) => {
const el = useRef(document.createElement("div"));
useEffect(() => {
// Use this in case CRA throws an error about react-hooks/exhaustive-deps
const current = el.current;
// We assume `modalRoot` exists with '!'
modalRoot!.appendChild(current);
return () => void modalRoot!.removeChild(current);
}, []);
return createPortal(children, el.current);
};
export default Modal;
- 错误处理
//option1 : 使用 react-error-boundary
//option2 : 自定义boundary component
import React, { Component, ErrorInfo, ReactNode } from "react";
interface Props {
children: ReactNode;
}
interface State {
hasError: boolean;
}
class ErrorBoundary extends Component<Props, State> {
public state: State = {
hasError: false
};
public static getDerivedStateFromError(_: Error): State {
// Update state so the next render will show the fallback UI.
return { hasError: true };
}
public componentDidCatch(error: Error, errorInfo: ErrorInfo) {
console.error("Uncaught error:", error, errorInfo);
}
public render() {
if (this.state.hasError) {
return <h1>Sorry.. there was an error</h1>;
}
return this.props.children;
}
}
export default ErrorBoundary;
31.联合类型的弊端,在对象与对象的联合时无法精准的进行区分
interface Admin {
role: string;
}
interface User {
email: string;
}
// Method 1: use `in` keyword
function redirect(user: Admin | User) {
if ("role" in user) {
// use the `in` operator for typeguards since TS 2.7+
routeToAdminPage(user.role);
} else {
routeToHomePage(user.email);
}
}
// Method 2: custom type guard, does the same thing in older TS versions or where `in` isnt enough
function isAdmin(user: Admin | User): user is Admin {
return (user as any).role !== undefined;
}
// Method ...: typeOf 和instanceof也可进行方便的类型保护
- 非空断言用法(最好是实际处理空值,并且尽量少用此法)
element.parentNode!.removeChild(element); // ! before the period
myFunction(document.getElementById(dialog.id!)!); // ! after the property accessing
let userID!: string; // definite assignment assertion... be careful!
- 用symbol创建标识性的ID注解
type OrderID = string & { readonly brand: unique symbol };
type UserID = string & { readonly brand: unique symbol };
type ID = OrderID | UserID;
function OrderID(id: string) {
return id as OrderID;
}
function UserID(id: string) {
return id as UserID;
}
function queryForUser(id: UserID) {
// ...
}
queryForUser(OrderID("foobar")); // Error, Argument of type 'OrderID' is not assignable
// to parameter of type 'UserID'
// unique 是一个关键词
// unique T(其中T是任何类型)允许在任何位置使用类型,并且名义上用标记标记T,使来自该位置的T只能分配给结果类型。
// 它是制造它的每个符号的唯一结构。然后通过交集将其混合到参数类型中,从而生成所有有用的关系
// 译文: 唯一符号的当前行为优先于语法上完全唯一的符号,然而,如果符号的一个名义子类实际上是需要的,你可以写
// Unique (symbol)来获得一个名义上的品牌符号类型(或symbol & Unique unknown -这是完全相同的事情)。唯一
// 符号的行为方式就像锁定在特定声明中的符号,因此在收缩和控制流时具有特殊能力。名义上的品牌类型在使用上更灵活,
// 但不具有强大的控制流链接的主机声明
// https://github.com/microsoft/TypeScript/pull/33038
// 实例:
// type NormalizedPath = unique string;
// type AbsolutePath = unique string;
// type NormalizedAbsolutePath = NormalizedPath & AbsolutePath;
// declare function isNormalizedPath(x: string): x is NormalizedPath;
// declare function isAbsolutePath(x: string): x is AbsolutePath;
// declare function consumeNormalizedAbsolutePath(x: NormalizedAbsolutePath): void;
// const p = "/a/b/c";
// if (isNormalizedPath(p)) {
// if (isAbsolutePath(p)) {
// consumeNormalizedAbsolutePath(p);
// }
// }
33.Overloading Function
// 1.
function pickCard(x: { suit: string; card: number }[]): number;
function pickCard(x: number): { suit: string; card: number };
function pickCard(x): any {
// implementation with combined signature
// ...
}
// 2.
type pickCard = {
(x: { suit: string; card: number }[]): number;
(x: number): { suit: string; card: number };
// no need for combined signature in this form
// you can also type static properties of functions here eg `pickCard.wasCalled`
};
34.获得组件的props类型可以使用React.ComponentProps
35.interface定义的{a:1,b:2}和typeof 获得的{a:1,b:2}类型意义是不一样的,因为前者不但校验了对象里value的类型还约束了值
36.js自动转换ts的工具
1.dts-gen
2.TypeStat
3.TypeWiz
4.js-to-ts-converter
5.TS-migrate used in Airbnb's conversion
37.自定义钩子的全局类型定义案例
declare module 'use-untyped-hook' {
export interface InputProps { ... } // type declaration for prop
export interface ReturnProps { ... } // type declaration for return props
export default function useUntypedHook(
prop: InputProps
// ...
): ReturnProps;
}
38.为类定义全局类型的案例
import * as React from "react";
declare class SimpleSelect extends React.Component<SimpleSelectProps, any> {}
export interface SimpleSelectProps {
autofocus?: boolean;
cancelKeyboardEventOnSelection?: boolean;
className?: string;
createFromSearch?(items: OptionValue[], search: string): OptionValue;
defaultValue?: OptionValue;
delimiters?: [any];
disabled?: boolean;
// ...
}
export default SimpleSelect;
- 内置类型
ConstructorParameters :类构造函数参数类型的元组
Exclude:将一个类型从另一个类型排除
Extract:选择可分配给另一类型的子类型
InstanceType:从一个新类构造函数中获得的实例类型
NonNullable:从类型中排除空和未定义
Parameters:函数的形参类型的元组
Partial:使对象中的所有属性都是可选的
Readonly:将对象中的所有属性设置为只读
ReadonlyArray:创建给定类型的不可变数组
Pick:对象类型的一种子类型,包含其键的子集
Record:从键类型到值类型的映射
Required:使对象中的所有属性都是必需的
ReturnType:函数的返回类型
41.如果你在库的官方类型中遇到bug,你可以将它们复制到本地,并通过“paths”字段告诉TypeScript使用你的本地版本。在你tsconfig.json
{
"compilerOptions": {
"paths": {
"mobx-react": ["../typings/modules/mobx-react"]
}
}
}